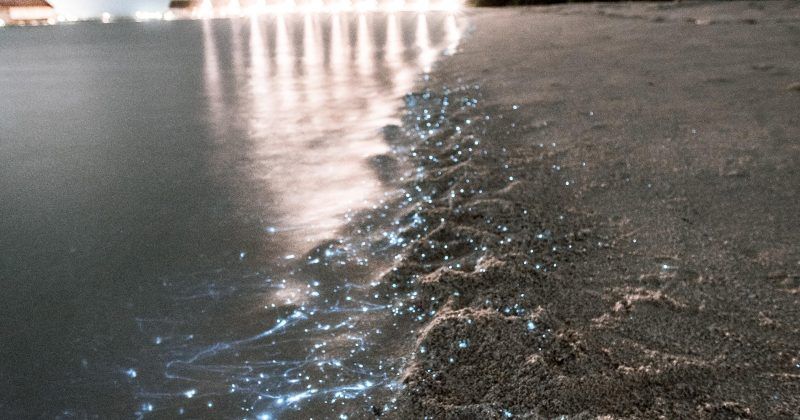
Bioluminescent Plankton
According to the Oxford dictionary bioluminescence is the ‘biochemical emission of light by living organisms’. It is a clever mechanism used by organisms to attract mates, find food and to respond to attacks.
About 80% of bioluminescent species live in the deep sea and it is estimated that most species that live 700 meters below sea level can produce their own light.
To produce their own glow-in-the-dark magic trick they use variations of a chemical reaction using three ingredients: an enzyme called luciferase, oxygen and luciferin.
This enzyme allows the oxygen to bond to the organic molecule luciferin. The high-energy molecule that is created releases the energy in the form of light.
These light producing molecules are interestingly good antioxidants and so it was believed that once they were used as such until they were eventually adapted for signalling. This is because as the oxygen content of the sea increased organisms were forced to dive to deeper depths away from...